
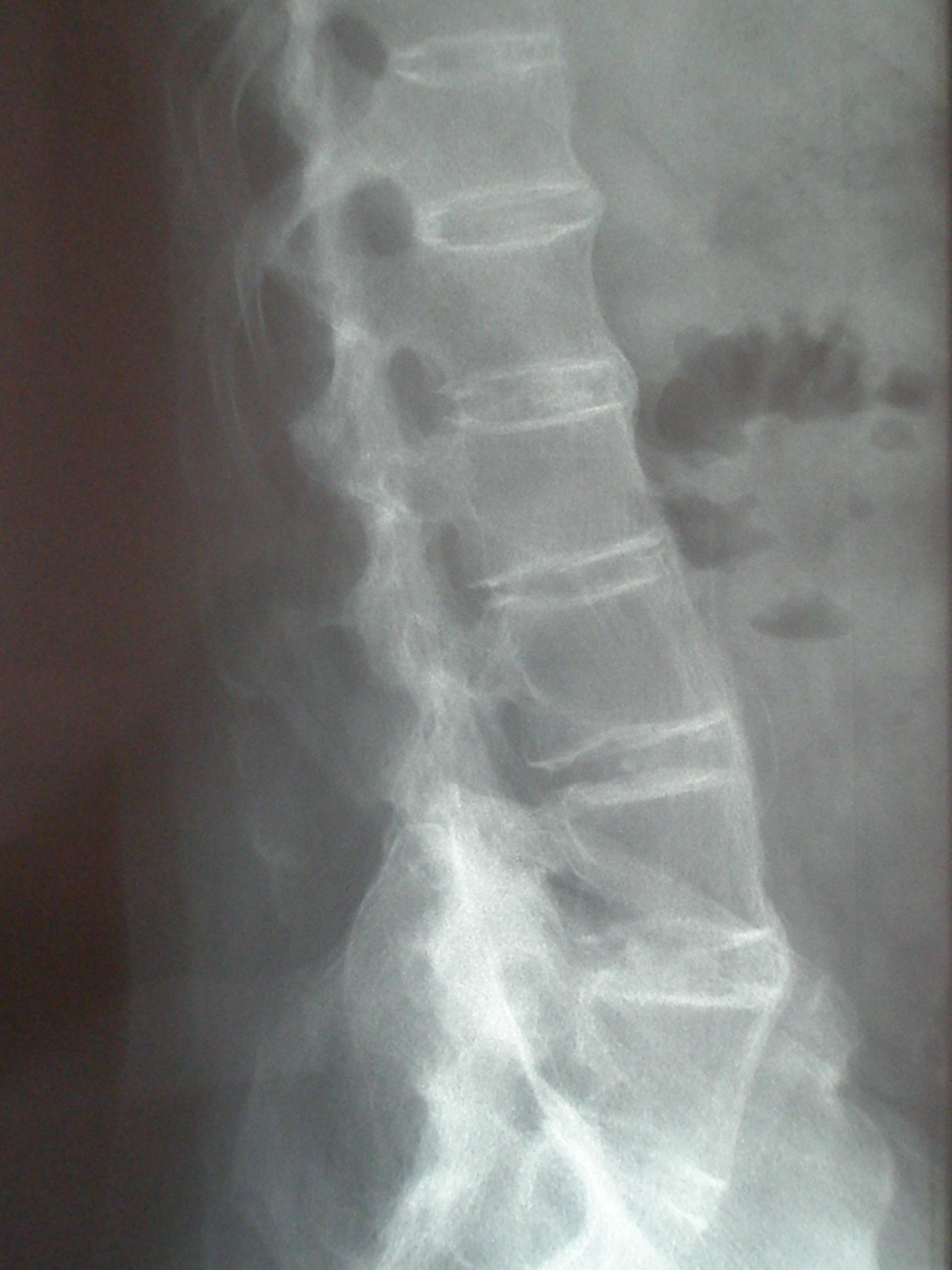
There is also accompanying squaring of the anterior vertebral body margins with associated reactive sclerosis of the vertebral body margins ( shiny corner sign) 5. The resulting radiographic appearance, therefore, is that of thin, curved, radiopaque spicules that completely bridge adjoining vertebral bodies. In a bamboo spine, the outer fibers of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral discs ossify, which results in the formation of marginal syndesmophytes between adjoining vertebral bodies 5. It is often accompanied by fusion of the posterior vertebral elements as well.Ī bamboo spine typically involves the thoracolumbar and/or lumbosacral junctions and predisposes to unstable vertebral fractures and Andersson lesions. The constellation of increased body weight, hip arthritis, and enthesitis may imply that mechanical stress contributes to radiographic damage in the presence of chronic inflammation.Bamboo spine is a pathognomonic radiographic feature seen in ankylosing spondylitis that occurs as a result of vertebral body fusion by marginal syndesmophytes. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that male sex, body mass index, hip arthritis, and enthesitis are associated with bamboo spine in axSpA.īamboo spine was more common in the male sex and associated with a delay in diagnosis, high BMI, hip involvement, and enthesitis. HLA-B27 status did not differ between groups. There was a tendency towards a more prevalent enthesitis in these patients. Hip arthritis, present or documented by a physician, was more common in Group 1. Male sex was more common among patients with bamboo spine. There were 111 patients (8.9%) with a bamboo spine. Out of the 5060 patients, 1246 had eligible radiographs. Data of patients with a bamboo spine (Group 1) was compared to data derived from patients with a longstanding disease of at least 15 years but no syndesmophytes (Group 2). Radiographs were assessed using the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiologic Index (BASRI). To analyse the clinical and laboratory factors associated with bamboo spine.ĭata of patients fulfilling the 2009 ASAS classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis, registered in the national, multicentre, longitudinal, and observational database of TReasure was analysed. 17 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Tekirdag Namik Kemal University, Tekirdag, Turkey.16 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Sakarya University, Sakarya, Turkey.15 Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Ministry of Health Adana City Training and Research Hospital, Adana, Turkey.14 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey.13 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Akdeniz University, Antalya, Turkey.12 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Hatay Mustafa Kemal University, Hatay, Turkey.11 University of Health Sciences, Gulhane Faculty of Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Ankara, Turkey.10 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Trakya University, Edirne, Turkey.9 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey.8 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Koc University, İstanbul, Turkey.7 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Health Sciences, Cam and Sakura City Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey.6 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Uludag University, Bursa, Turkey.5 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Marmara University, Hatay, Turkey.

4 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Yıldırım Beyazıt University, Ankara, Turkey.3 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Izmir Katip Celebi University School of Medicine, Izmir, Turkey.2 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey. 1 Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Marmara University, Hatay, Turkey.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
